The interaction between Delta-9 THC and anti-inflammatory diets is really quite enlightening in the health journey. Thus, Delta-9 THC might be related to immune system modulation, possibly enhancing the effectiveness of an anti-inflammatory diet. Such an association might reduce chronic inflammation but also improve general well-being.
These relationships open the door for potential therapeutic applications, so it is important to follow up on new research and practical dietary strategies.
What is Delta-9 THC?
Delta-9 THC is among the most occurring cannabinoids known to result in psychoactivity. This involves a discussion of its chemical properties, biological activity, and effects towards the endocannabinoid system.
Chemical Properties and Biological Activity
Delta-9 THC, or delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, has the chemical formula C21H30O2. Mostly, it is associated with an antagonistic activity above cannabinoid receptors in the brain and body.
- Molecular Structure: Its structure of atoms in its specific shape allows Delta-9 THC to have specific interactions with receptors, which thus influence several physiological processes.
- Psychoactive Effects: It produces euphoria, changing the mood and perception of things. This is mainly because of the interaction with CB1 receptors in the brain.
- Anti-inflammatory Potential: Research has also shown that Delta-9 THC may help reduce inflammation, which becomes necessary in anti-inflammatory diets. Its ability to modulate immune responses in many instances can be mitigative against certain health conditions.
Interaction with Endocannabinoid System
The ECS is therefore instrumental in the establishment of homeostasis in an organism. Delta-9 THC acts at two receptor types, primarily the CB1 and CB2 receptor types.
- CB1 receptors are mainly found within the brain, and they are responsible for the psychoactive effects of Delta-9 THC. Activation of these receptors might influence mood, possibly memory, and also pain perception.
- CB2 Receptors These are almost exclusively to the immune system. The interaction of Delta-9 THC with CB2 receptors is relevant to the anti-inflammatory activity and is a great resource for anyone interested in anti-inflammatory diets.
It is the balance between activating the CB1 and CB2 receptors that determines the overall effect Delta-9 THC has on the body, both on mood and inflammation.
Delta-9 THC in the Cannabis Sativa Plant
Delta-9 THC is a natural chemical constituent of the Cannabis Sativa plant. It is the most researched cannabinoid, which has much health-related implication.
- Concentration: The concentrations of Delta-9 THC differ with any specific strain of Cannabis Sativa. High-THC types are used for pharmaceutical and therapeutic use.
- Cultivation and Extraction: The preferred method of farming is for specific strains to get a higher level of THC. Popular extraction methods to get the potent form of this cannabinoid include CO2 extraction.
- It has anti-inflammatory effects that may prove useful for diets expected to suppress chronic inflammation; hence, a potential area of research and attention for researchers and health enthusiasts.
Understanding delta-9 THC and its role in the Cannabis sativa plant increases your knowledge of its applications in health and wellness.
What Role Does Anti-Inflammatory Diet Play?
Anti-inflammatory diets play an essential role in managing chronic inflammation and related metabolic disorders, so you can focus on a few of the components and their effects in your body to develop an appropriate nutritional strategy for an overall healthy lifestyle.
Components of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
These are foods that tend to suppress the underlying inflammation of the body. Key ingredients in such foods include
- Fruits and Vegetables: They have antioxidants, vitamins, and fibers. The best are berries, leafy green ones, and the cruciferous ones.
- Healthy Fats: Omega-3 fatty acids in olive oil, fatty fish, and nuts possess anti-inflammatory effects.
- Whole Grains: They include food such as brown rice, quinoa, and oats, which contain higher fiber content and nutrients than the refined grains.
- Herbs and spices: Turmeric and ginger contain compounds that can lower inflammation markers in your body.
These components now work synergistically to promote lower inflammation levels and effectively reduce your risk of chronic diseases.
Effects on Chronic Inflammation and Metabolic Disorders
It is somehow related to other metabolic diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular conditions. All these risks can be addressed through an anti-inflammatory diet.
Available evidence indicated that a diet of anti-inflammatory foods regularly may:
- Decrease the inflammatory markers like C-reactive protein.
- Improves insulin sensitivity and blood sugar levels.
- Induce weight loss and reverse diet-induced obesity.
This anti-inflammatory diet would address all the pathological processes that lead to these conditions and thus seek a better metabolic health condition.
Diet and the Gastrointestinal Tract
The function of the gut is significant when considered for anti-inflammatory management. Balancing an anti-inflammatory diet promotes proper gut health through
- Fiber Intake: Soluble fiber obtained from vegetables, fruits, and whole grains feeds good gut bacteria, making it more effective in fighting inflammation.
- Fermented Foods: Yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut have probiotics, which will balance gut microbiota and push out inflammation.
- Hydration is essential to ensure the gut and mucosal lining work and function normally.
These will help the health of your gut system, where reduction in systemic inflammation and promotion in your general welfare can be gained.
What is the Immune Response of Delta-9 THC?
Interaction Patterns of Delta-9 THC with the Immune System: VERY COMPLEX. This relates to its interaction with many immune cells and the related functions, such as cytokine production, dendritic cells, T cells, etc., and the peripheral nervous system.
Cytokine Production and Inflammatory Cytokines
Cytokines are the signaling molecules of much of an immune response. Delta-9 THC is a modulator of inflammatory cytokine production, like TNF-alpha or IL-6, that normally are elevated in inflammatory diseases.
One can only hypothesize that THC possibly reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines, thus further reducing inflammation. The potential to regulate the balance towards anti-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-10, justifies the therapeutic role of THC in inflammatory diseases. These changes could affect how one reacts to various immune challenges.
THC's Impact on Dendritic Cells and T Cells
THC Effect on Dendritic Cells and T-Lymphocytes Dendritic cells could trigger an immune response at the stages of maturation and activation in vitro. At the cellular and molecular level, delta-9 THC also affects presenting an antigen to T-cells effectively.
Studies demonstrate, lowers the activation and proliferation of T cells by THC. This would be a desirable state if excessive immune activity is pathologically deleterious, such as in autoimmune diseases. However, if it causes suppression, its balance must be struck such that it will not also interfere with host responses to pathogens.
Modulation of the Peripheral Nervous System
The peripheral nervous system plays another important role in the immune response and inflammation of the body. It also interacts with the delta-9 THC in interaction with the endocannabinoid system containing receptors in the PNS. Manipulation in pain and inflammatory response signaling may occur.
THC has been proven to reduce neuroinflammation. It may be beneficial for a neuropathic pain condition. By modulating the PNS, THC can control the inflammation and improve pain management. Understanding these effects can help in harnessing its potential in therapeutic applications.
What are the Potential Therapeutic Applications of Delta-9 THC?
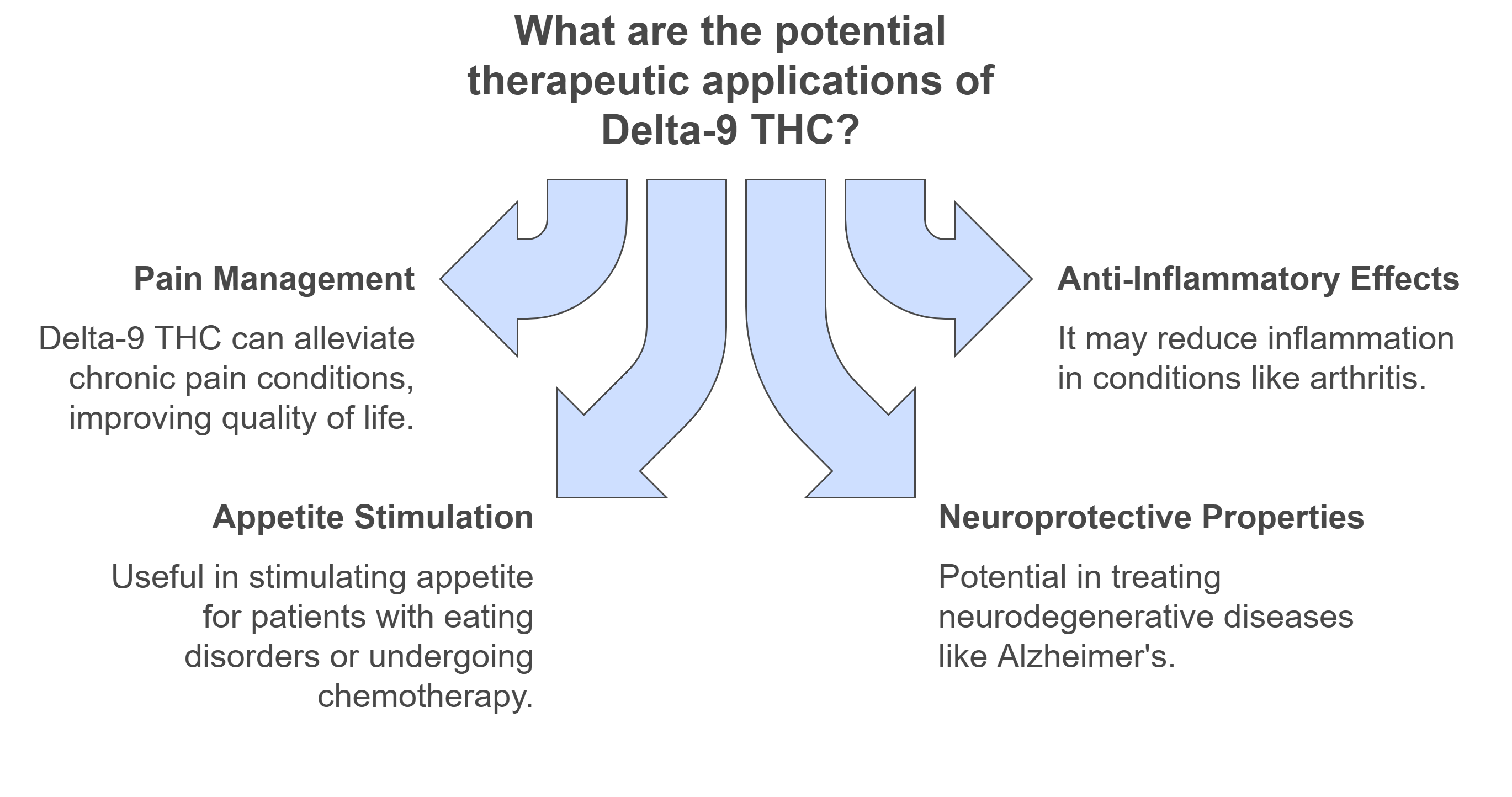
Major therapeutic potential areas of Delta-9 THC are associated with anti-inflammatory effects. Research focus spots include influences that this cannabinoid has on inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, specific conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis, and neurological disorders.
THC for Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases
Delta-9 THC interacts with the endocannabinoid system, implicated in immune response regulation. This interaction may suppress inflammation by way of modulating cytokine production, thus playing a role in pathways that involve inflammation.
Research has shown that THC can reduce the severity of symptoms caused by different inflammatory disorders. The anti-inflammatory effects may reduce tissue damage and improve the quality of life for people suffering from such conditions. An anti-inflammatory diet with THC may be even more beneficial.
Rheumatoid Arthritis and Multiple Sclerosis
In rheumatoid arthritis, THC reduces pain and inflammation within the arthritic joints. The clinical studies showed that the high-THC content products were adopted by patients whose symptoms were milder.
For multiple sclerosis, THC may ease muscle spasticity and pain. Some patients also report an improvement in their mobility and reduced discomfort, which indicates THC's potential in symptom management. Jointly using THC with an anti-inflammatory diet may create a synergistic effect, further supporting patient well-being.
Anti-Inflammatory Potential in Neurological Conditions
Emerging evidence suggests that THC's anti-inflammatory properties may benefit neurological conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
These conditions are accompanied by chronic neuroinflammation, and THC may neutralize this inflammation. For example, patients improve in cognitive function alongside reduced neural deterioration. The combination of smoking THC with an anti-inflammatory diet will enhance these protective effects on the nervous system.
Conclusion
The use of Delta-9 THC in anti-inflammatory diets has been promising for diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease and metabolic diseases. It acts with CBD and THC from the cannabis plant to inhibit inflammatory activation by interfering with pathways that involve reactive oxygen species and cytokine secretion.
The most recent research on in vitro models and murine models presents how it modulates innate immunity, increases the cell's viability, and decreases systemic inflammation. Delta-9 THC can be the answer to eliminating symptoms from fatty liver disease and systemic lupus erythematosus, a gateway that can treat chronic inflammation to a life of betterment.


